Top Guide Sensor Negatives
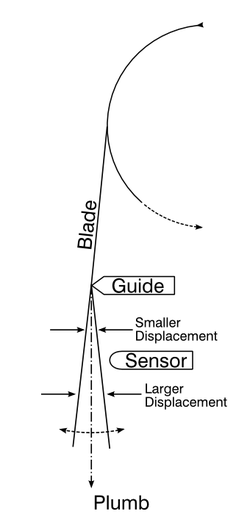
A big disadvantage of the top guide proximity sensors is they cannot measure any deviation in blade position at all, at the saw guide, since the guides are solid and the saw is prestrained firmly against the guide. Instead, as shown at right, the top guide sensor measures how far the blade departs from plumb at a position below the guide. As the example figure shows, only a very small deviation is available to measure near the saw guide. This deviation is not representative of the blade’s deviation in the workpiece, and yet even measuring this small displacement requires that the saw guide be positioned further away from the wood (so that there is room for the sensor between the guide and the workpiece). This arrangement conflicts with the preference for running the guide closer to the wood for a stiffer saw. The top guide proximity requires a longer span between guides to accommodate the proximity sensor, and thereby introduces greater potential for blade deviation.
A big disadvantage of the top guide proximity sensors is they cannot measure any deviation in blade position at all, at the saw guide, since the guides are solid and the saw is prestrained firmly against the guide. Instead, as shown at right, the top guide sensor measures how far the blade departs from plumb at a position below the guide. As the example figure shows, only a very small deviation is available to measure near the saw guide. This deviation is not representative of the blade’s deviation in the workpiece, and yet even measuring this small displacement requires that the saw guide be positioned further away from the wood (so that there is room for the sensor between the guide and the workpiece). This arrangement conflicts with the preference for running the guide closer to the wood for a stiffer saw. The top guide proximity requires a longer span between guides to accommodate the proximity sensor, and thereby introduces greater potential for blade deviation.
